Well, we all know how terrible it is to lose something important for which you are working very hard only because the document is not saved properly.
Oracle database has recently added a lot more features to reduce the chances of losing data due to accidental deletion, crashes or accidental deletions, etc. that feature is maintaining the auto-backup of oracle database data.
In this article, we will explore different types of Oracle Backup And Recovery options to safeguard your oracle data completely.
What Are The Different Types Of Oracle Backup And Recovery Options Available?
Mainly there are four different types of Oracle backup and recovery options available. All four types of backup options are given here so follow them strictly for the right Oracle backup and recovery.
-
Cold backup:
If your database is in no archive log mode, then you can go with cold backup. For taking cold backup follow the given steps to perform a successful backup:
- Shutdown the database
Sql>shutdown immediate;
- Manually copy the data files, control files, and redo log files to your desired destination.
- Start the database
Sql>startup;
-
Hot backup:
If your database is in archive log mode, then you can go with hot backup without any database outage.
- Execute the following command if you want to get the logs for hot backup in a separate log file.
- Begin hot backup by executing the following command.
Sql>alter database begin backup;
- Manually copy data files, control files, and redo log files to your desired destination without shutting down the database.
- Stop the hot backup by executing the following command.
Sql>alter database end backup;
- Switch the log file after completing the hot backup.
Sql>alter system switch logfile;
Copy archive files that are used to recover the database.
Copy this command to recover the database:
sql>recover database using control file auto backup until cancel;
-
RMAN Backup:
Target the database which we are going to take the backup.
Recovery catalog is the destination, which stores the information about the target database.
- RMAN Without recovery catalog:
Requirements for RMAN backup:
- The database must be in archive log mode.
- Copy the following command to connect to the target database without a recovery catalog. After connecting to the target or auxiliary database you will have the SYSDBA privilege.
- To have the complete backup of the database copy the following command.
- RMAN>backup database;
- To take a backup of tablespace use the below command
Rman>backup tablespace tablespace_name;
- To have the backup of datafile copy the following command.
Rman>backup datafile ‘C:\oracle\product\10.2.0\oradata\orcl\datafile_name’;
By default, all these backups will get stored in flash_recovery_area.
Recovery operation using RMAN:
- To see the list of backups use the below command.
Rman>list backupset;
2.It’s not possible to retrieve the data from the backup set. Therefore, you need to validate the backup set.
To check whether the backup set is valid or not, copy the following command.
Rman>validate backupset list_number;
Shutdown the database and put it in the mount mode to recover the database.
Rman>recover database;
-
Import – Export Backup:
Data guard is the new feature in Oracle 10g that lets you transfer data from one location to another at high speed.
It consists of two utilities:
1. Export utility: It is used to store the database objects in the storage media like disks outside the database.
Export operation:
1. Create the directory
C:\>mkdir c:\backup
- Connect to the database and create the directory for backup
Sql>create directory backup as ‘c:\backup’;
The directory created.
- Now move to the host mode.
Sql>host - Go to the directory C:\oracle\product\10.2.0\db_1\BIN
C:\>cd C:\oracle\product\10.2.0\db_1\BIN - Execute the export command.
C:\oracle\product\10.2.0\db_1\BIN> expdp sys/test directory=bkup dumpfile=bfull.dmp logfile=bfull.log full=y
2. Import Utility: It is used to load the objects to the database from the storage media.
For the import operation execute the below command.
C:\oracle\product\10.2.0\db_1\BIN> impdp sys/test directory=bkup dumpfile=bfull.dmp logfile=bfull.log full=y
How To Recover Oracle Database When There Is No Backup?
If you faced the data loss issue and don’t have a proper backup then in order to recover the data you can go with Oracle Database Repair Tool.
It’s a professional tool to get back your inaccessible data from an error showing or corrupt Oracle database. This recovery application is also suggested by lots of professionals because it is easy to use and an effective solution to deal with a completely corrupt Oracle Database.


- This recovery tool provides complete assurance of zero percent data loss on restoring your data.
- It repairs damaged or corrupt. DBF file and restores your important data with ease.
- This tool searches the entire Oracle databases that present in the computer system, it also displays the preview of recoverable database objects after scanning the corrupt file.
- You can also do selective recovery of DBF components.
- This recovery tool is compatible with Windows 7, Vista, XP, 2008, 2003, and 2000.
- It is designed with a strong algorithm and has effective scanning and recovery technology.
You also don’t need a backup of your database to restore Oracle database. So, it is recommended to try this recovery application once and get back your precious data.
If you don’t have deep knowledge about the Oracle database but want to restore data from a corrupt oracle database then this recovery application is best for you. Its simple user interface allows the normal user to operate it and get back their data.
Steps To Use Oracle Database Repair Tool Restore Oracle Database File
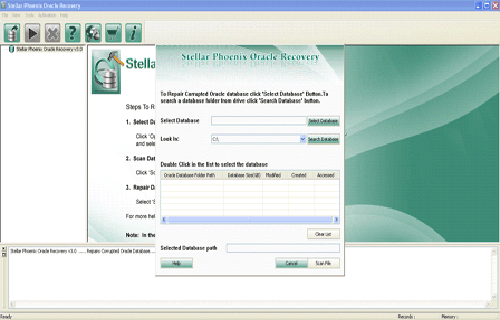
Step 1: Search the initial screen of Oracle Database Repair Tool with a pop-up window showing options to select or search corrupt Oracle databases on your computer.
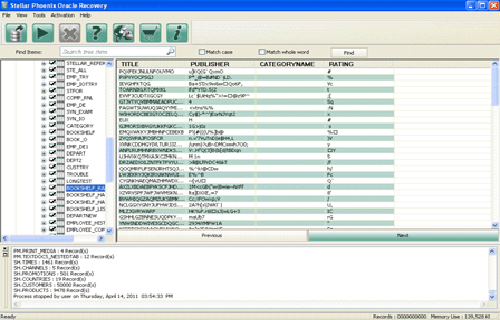
Step 2: Click Scan File to initiate the scan process after selecting the oracle database. The recoverable database objects get listed in left-side pane.
Step 3: Click an object to see its preview.
Step 4: : Click Start Repair in the icon bar to start the repair process. A pop-up window is displayed which shows the steps needed to perform further. Click next and continue.
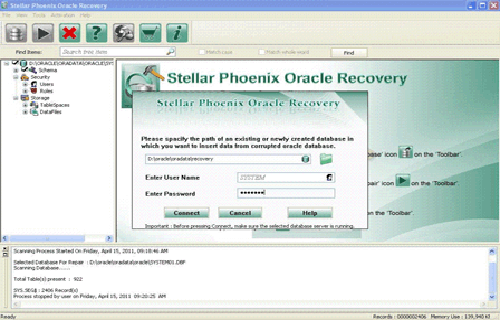
Step 5: Give the user name, password, and path of the blank database where you want to save the repaired database objects.
Step 6: Repairing and restoring various database objects after establishing a connection with a blank Oracle database.
How To Keep Your Oracle Database Secure?
Trick to Secure User accounts:
- Strictly limit the SYSTEM and OBJECT privileges.
- Avoid giving needless access to database users.
- Limit the number of users who can create, alter, or delete database objects.
- Provide CREATE ANY JOB, EXP_FULL_DATABASE, and BECOME USER privilege only to the needy users.
- The CREATE PUBLIC SYNONYM and DROP PUBLIC SYNONYM are provided only to trusted users.
Tricks to Secure Data:
- Defend the data dictionary because any alteration is done in it, then it can harshly affect the database performance.
- Protect the data dictionary with the help of, set 07_DICTIONARY_ACCESSIBILITY = FALSE.
- Always set the admin password on your system.
- Provide the path or file to the database carefully to avoid any modification from anyone.
- Files and their path accessibility must be given only to DBA.
Tricks to Secure Roles:
- Make global roles for enterprise users.
- Programmers must not be given user roles.
- Categorize roles as per the user job accountability.
Tricks to Secure the Network:
- Always use the Firewall, it will help in avoiding database from external access.
- Set the firewall to recognize data only from trusted or safe sources.
- Utilize Enterprise Manager Database Control at the time monitoring listener action.
- Avoid setting passwords in the listener.ora file.
- Pass up Oracle listener from illegal access.
Wrap Up:
Enabling these Oracle backup and recovery option will hopefully prevent you from getting into situations like losing important data.
Maintaining oracle backup in cloud storage or one-drive gives extra safety to your data from PC or database catastrophic failure like situations. So try to make a habit of maintaining proper Oracle database backup.
If you have a question regarding any other Oracle database error or issue then, feel free to ask in the below comment section.

Jacob Martin is a technology enthusiast having experience of more than 4 years with great interest in database administration. He is expertise in related subjects like SQL database, Access, Oracle & others. Jacob has Master of Science (M.S) degree from the University of Dallas. He loves to write and provide solutions to people on database repair. Apart from this, he also loves to visit different countries in free time.